-
What is email impersonation?
Email impersonation is a phishing technique. Cybercriminals create email addresses that look legitimate to trick their targets into trusting them.
Email impersonation might not be the most sophisticated phishing method, but it’s simple, it’s widespread, and it can be devastating. Here’s why…
Email impersonation vs. email spoofing vs. account takeover
First, we need to describe “email impersonation” and distinguish it from some closely-related concepts.
- Email impersonation: The attacker sets up an email address that looks like a legitimate email address (e.g. bill.gates@micr0soft.com – note the zero instead of an o in the domain name).
- Email spoofing: A technical process where the attacker modifies an email’s headers so the receiving email client displays a false email address (the sender’s email address is “fraudster@cybercrime.com,” but the recipient sees “billgates@microsoft.com” in their inbox)
- Account takeover: The attacker gains access to another person’s account (using hacking or stolen credentials) and uses it to send phishing emails.
Email spoofing and account takeover require some technical ability (or, at least, access to the dark web). With email impersonation, though, the attacker just needs to secure a domain that looks like it could belong to a legitimate business.
This is easy (and cheap!) with domain registrars like GoDaddy. We explore different types of impersonation techniques below.
Phishing methods that use email impersonation
Cybercriminals can use email impersonation to facilitate any type of email-based phishing attack. There are some types of phishing in which email impersonation is particularly common, including:
These are all among the more sophisticated and targeted types of phishing attacks. These types of attacks must employ email impersonation, email spoofing, or account takeover to be successful.
Types of email impersonation
Now we’ll look at the various ways a cybercriminal can impersonate an email address. To understand these, you’ll need to know about the different parts of an email address:
Each of these elements of an email address is relevant to a different type of email impersonation.
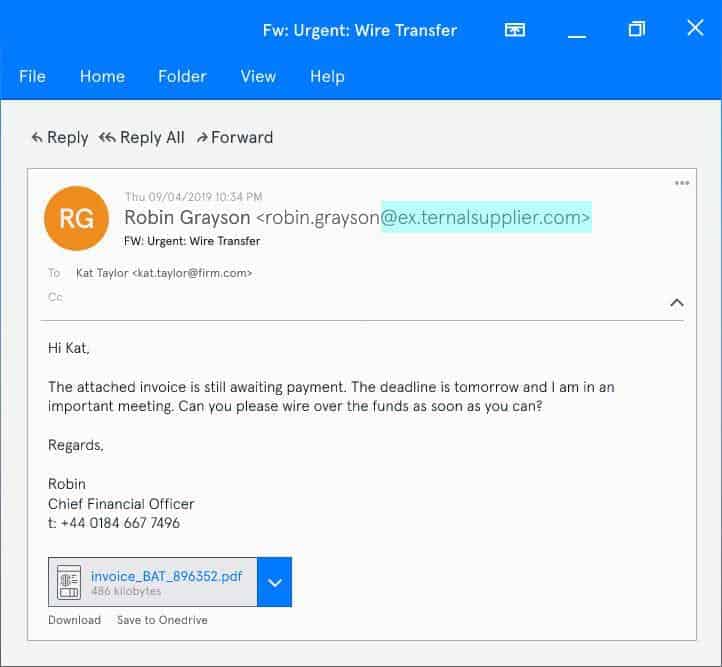
Root domain-based email impersonation
A company’s root domain is usually the most distinctive part of its email address. It’s the part immediately before the top-level domain (e.g. “.com”) — the “Amazon” in “info@amazon.com”.
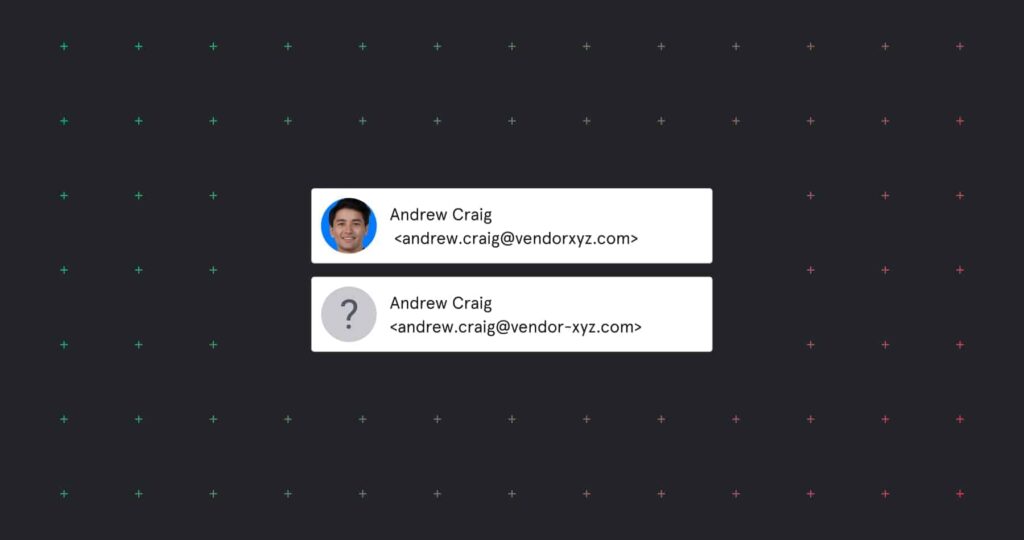
Root domain impersonation involves creating a root domain using replacement characters, so it looks like an email has arrived from a legitimate company. Here’s an example.
This is an example of a root domain impersonation.
In this root domain impersonation, the attacker has replaced the “l” in “external” and “supplier” with a “1”. At first glance, the recipient might not notice this, and they might treat the email as though it has come from “External Supplier.”
Top-level domain-based email impersonation
The top-level domain is the part after the root domain: e.g., “.com”, “.jp”, or “.net”. The top-level domain usually denotes a country or a type of organization. For example:
- .com — Commercial organizations
- .uk — Internet country code for the UK
- .gov — US government agency
Sometimes, a second-level domain accompanies a top-level domain:
- .co.uk — Commercial organization from the UK
- .ac.jp — Higher education institution from Japan
- .waw.pl — Organization from Warsaw, Poland
Using top-level domain impersonation, a cybercriminal can create an authentic-looking email address that the recipient might assume belongs to a legitimate organization (if they even notice it).
Here’s an example:
This is an example of top-level domain impersonation
Here we have “externalsupplier.io” imitating “externalsupplier.com”. The top-level domain “.io” is actually registered to British Indian Ocean Territory (BIOT), but Google recognizes it as “generic” because many non-BIOT organizations use it.
Subdomain-based email impersonation
A subdomain appears after the “@” sign, but before the root domain. For example, in “info@mail.amazon.com”, the subdomain is “mail”. Most email addresses don’t have a subdomain.
An attacker can use subdomains to impersonate a legitimate company in two main ways:
- Using a company’s name as a subdomain to the attacker’s domain. For example, in “info@amazon.mailerinfo.com”, “amazon” is the subdomain and “mailerinfo” is the domain.
- Splitting a company’s name across a subdomain and domain.
Here’s an example of the second type of subdomain impersonation:
This is an example of subdomain impersonation
Display name impersonation
A display name is how an email client shows a sender’s name. You can choose your display name when you sign up for an email account. We explore display name impersonation in more detail in this article: How to Impersonate a Display Name.
Display name impersonation exploits a bad habit of mobile email clients. On mobile, common email clients like Outlook and Gmail only display a sender’s display name by default. They don’t display the sender’s email address.
So, even an email address like “cybercriminal@phishing.com” might show as “Amazon Customer Services” in your mobile email client — if that’s the display name that the attacker selected when setting up the account.
But this isn’t a mobile-only problem. According to new research, just 54% of employees even look at the email address of a sender before responding or actioning a request. This is good news for attackers, and bad news for businesses.
Username impersonation
The username is the part of the email address that appears before the “@” symbol. For example, in “bill.gates@microsoft.com”, the username is “bill.gates”.
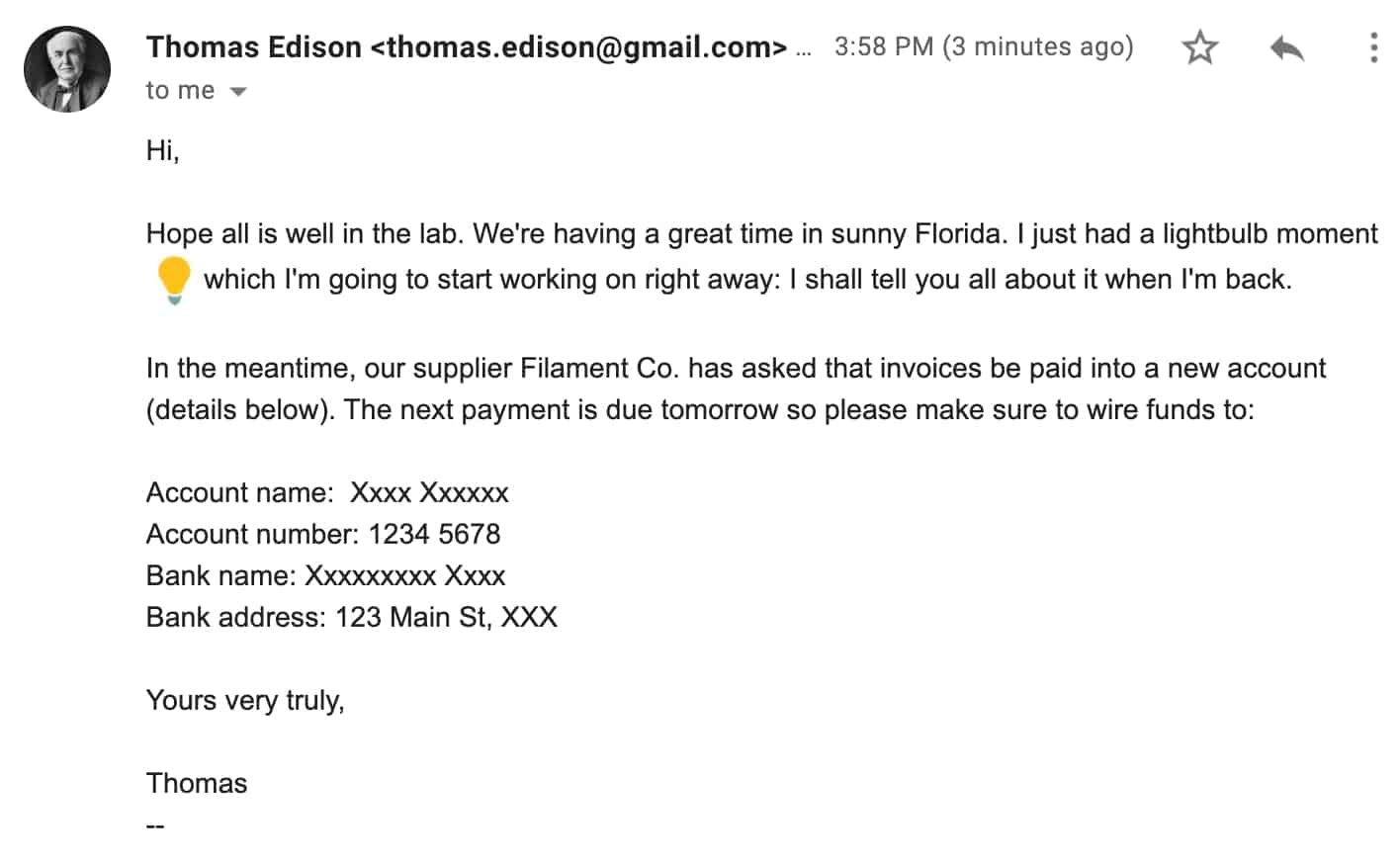
Username impersonation is the least sophisticated form of email impersonation, but it can still work on an unsuspecting target. This technique is sometimes called “freemail impersonation,” because scammers can register false usernames with Gmail or Yahoo.
With this technique, they can create accounts that look like they could belong to your CEO, CFO, or another trusted person in your network.
Here’s an example:
This is an example username impersonation and display name impersonation
More resources on email impersonation
Now you know the basic techniques behind email impersonation, read our articles on preventing email impersonation, CEO fraud, and Business Email Compromise to find out how to protect your business from these cyberattacks.
You can also learn how Tessian detects and prevents advanced impersonation attacks by reading our customer stories or booking a demo. Not quite ready for that? Sign-up for our newsletter below instead. You’ll be the first to know about new research and events and get helpful checklists and how-to guides straight to your inbox.