Summary
Tessian Threat Intel is issuing a threat advisory on cyber threat actors requesting payment from unsuspecting victims using fraudulent invoices issued via PayPal. We have alerted PayPal.
Overview
Tessian Threat Intel analysts have observed scammers, on numerous occasions, sending emails with fake invoice payment requests. Historically many of these sorts of attempts would be detected by traditional spam filters and end up in the junk folder or in quarantine. This is due to the email senders being repeat offenders with the same template and text – easily detected as spam or malicious by rule based email security solutions.
Since early March 2022, Tessian identified ways in which threat actors have been adapting their techniques to reach victim’s inboxes by abusing the legitimate capability of sending invoices to 3rd parties using PayPal’s email-delivered invoicing services.
To be clear, this is not a vulnerability within PayPal. Nor is it an example of an account takeover (ATO). Rather, threat actors are creating invoices in PayPal and then issuing them to victims through PayPal’s service.
Technically, an email from PayPal would pass some of the most fundamental checks in email security like SPF, DMARC and DKIM. This would ensure with a high degree of probability that similar emails would avoid detection by rule based email security solutions, as well as giving an air of legitimacy to the email.
An email sent from a financial services provider like PayPal, would increase the probability of the victim seeing and interacting with the email, including acquiescing to its demands for payment.
Examples of fraudulent PayPal invoices
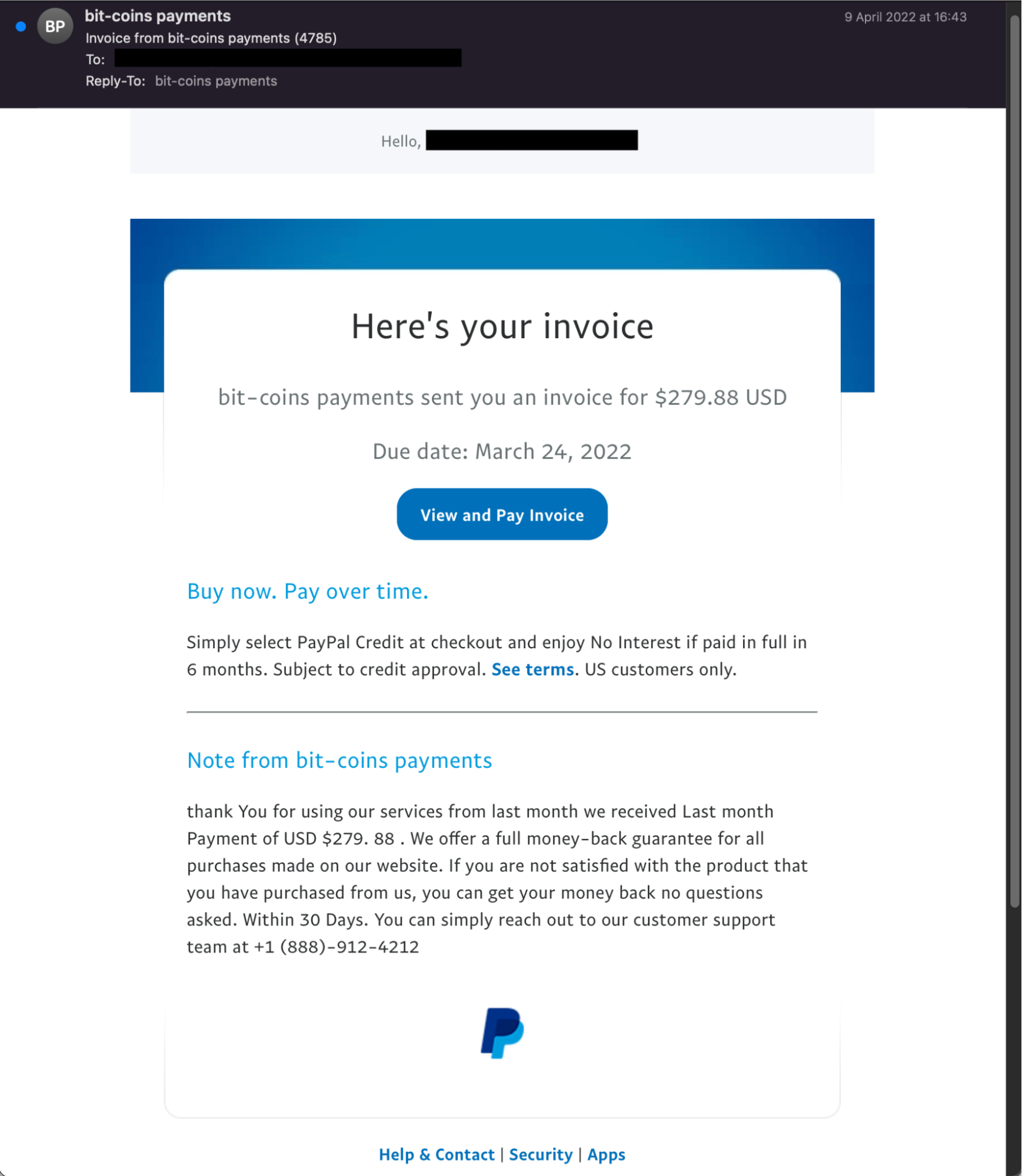
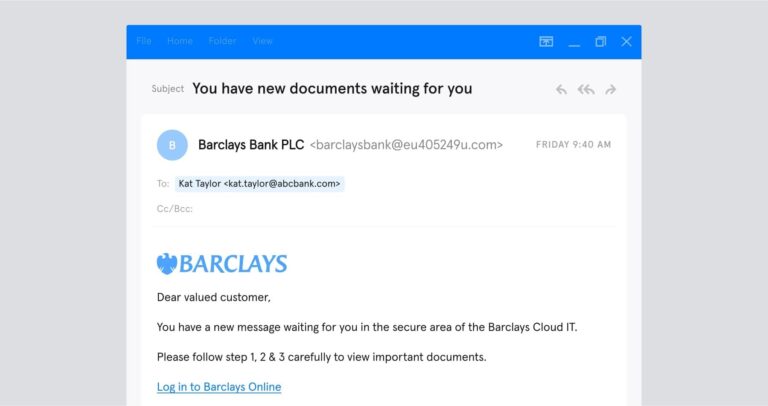
The screenshot below is a legitimate email from PayPal containing a fraudulent invoice. In this example, the attacker has created a paypal account with the profile name “bit-coins payments,” which is displayed as the sender display name.
The threat actor has then created an invoice using the invoicing service available in PayPal (see Fig 2), and has then sent it with a message added by the attacker for the recipient. Grammatical style errors can also be observed, similar to what we have seen in common phishing emails.
Fig 1: Example of fraudulent PayPal invoice
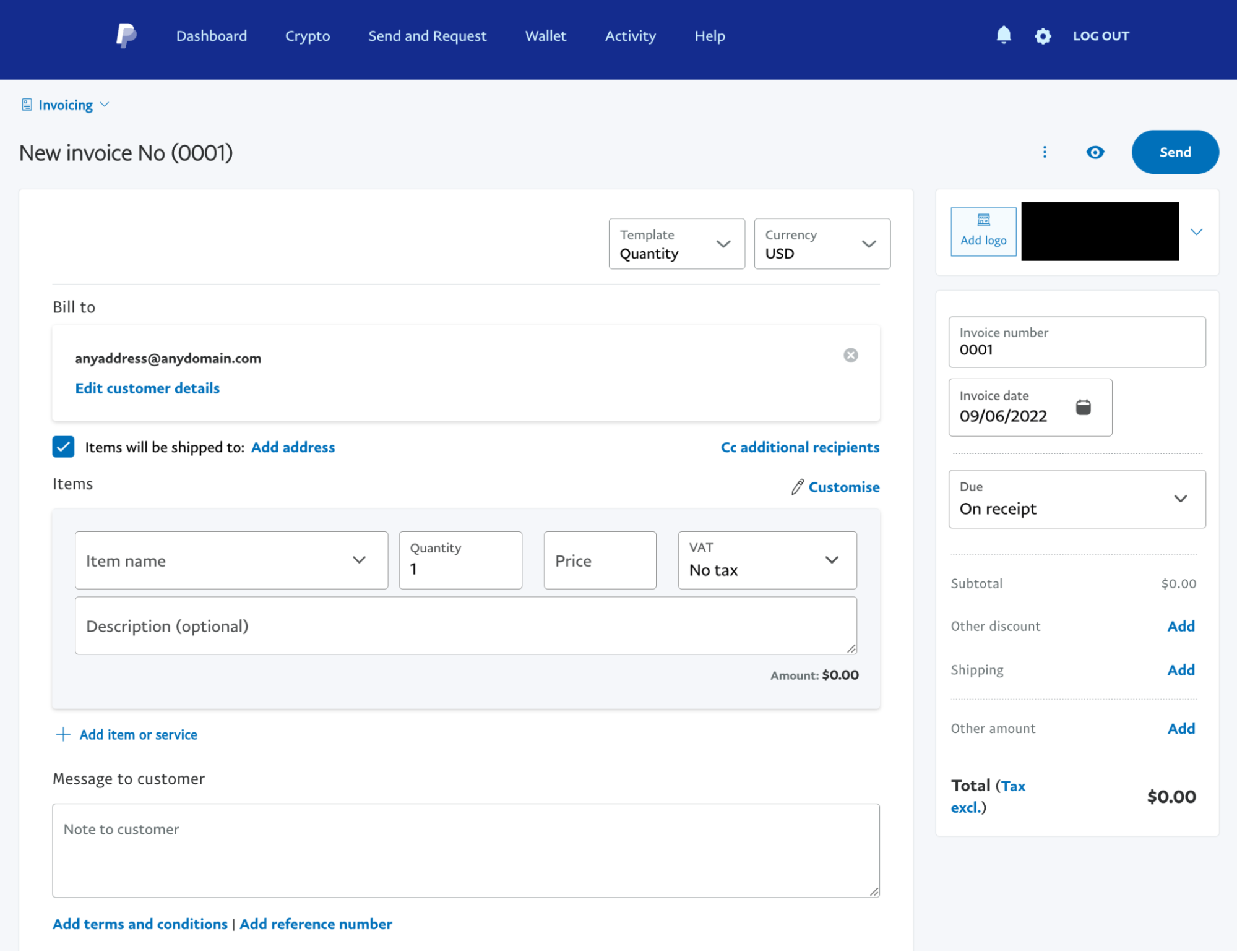
The below screenshot shows the PayPal invoicing service.
Fig 2: PayPal invoice issuing feature
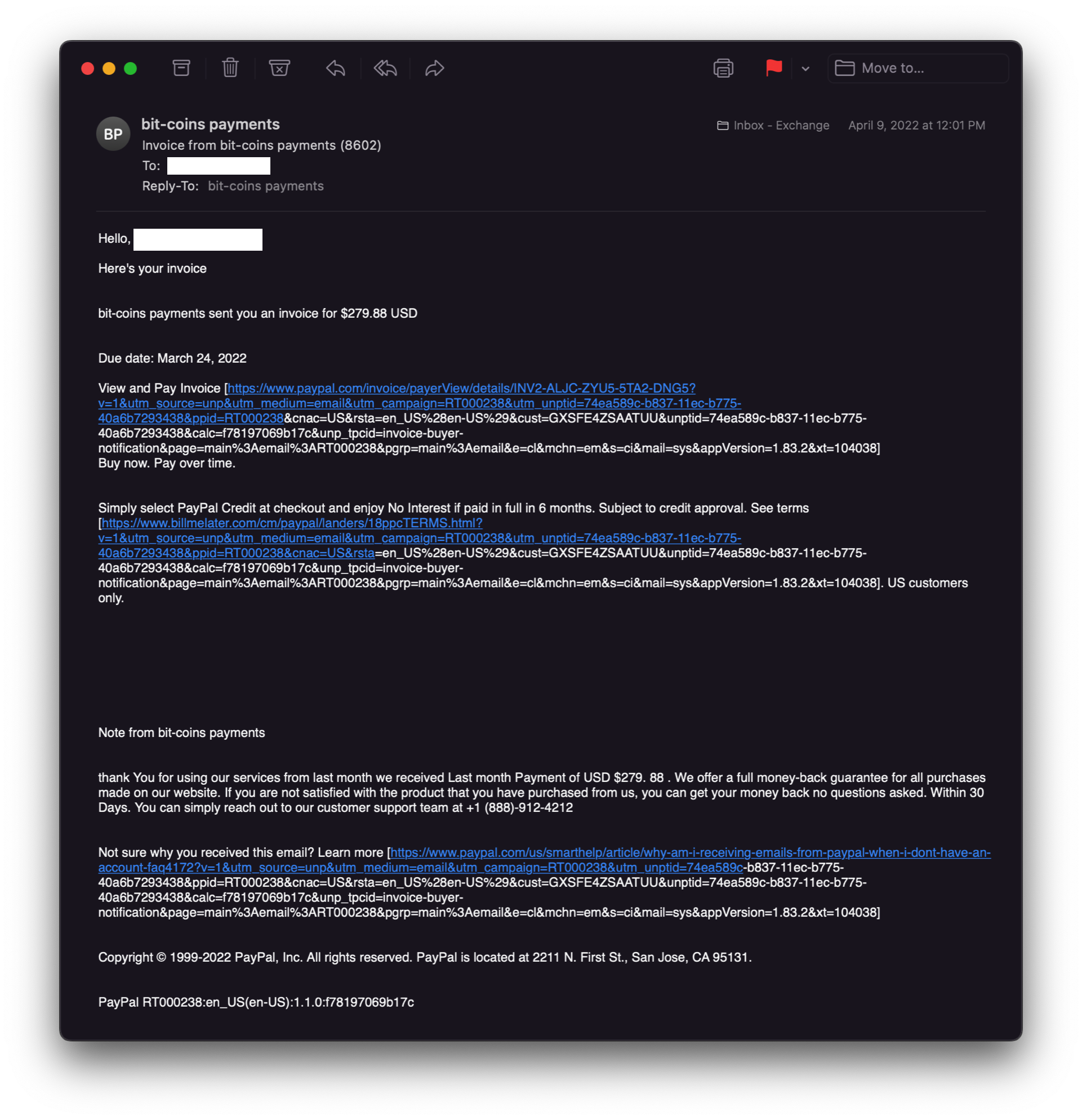
In the example below, we can see the actual link addresses which would redirect the recipient to the PayPal generated invoice if clicked.
Fig 3: Malicious email requesting Bitcoin payment with links to fraudulent PayPal invoice
Technical breakdown of the message headers
As you can see below, both SPF and SKIM are a pass, and the sender IP ties back to PayPal directly. This sort of email has a high probability of passing rule based email security solutions and being delivered into a victim’s inbox.
Authentication-Results: spf=pass (sender IP is 173.0.84.227)
smtp.mailfrom=paypal.com; dkim=pass (signature was verified)
header.d=paypal.com;dmarc=pass action=none
header.from=paypal.com;compauth=pass reason=100
Received-SPF: Pass (protection.outlook.com: domain of paypal.com designates
173.0.84.227 as permitted sender) receiver=protection.outlook.com;
client-ip=173.0.84.227; helo=mx2.slc.paypal.com;
Threat Mitigation Steps
Once PayPal was informed, Tessian found that the invoice was taken offline and no longer accessible. Thank you PayPal for your quick engagement.
In order to not fall victim to similar types of email-delivered invoice fraud we recommend:
- Be careful of unsolicited emails, especially those containing requests for payment or including links to invoices.
- Always verifying the authenticity of an invoice with the actual purchase order.
- If necessary, contact PayPal or any vendor requesting payment via independent method i.e. telephone to verify the authenticity of the request.
- Have a failsafe system in place in your accounting department that requires two members of staff to verify the authenticity of invoices matched against purchase orders.
- Adopt intelligent cloud email security solutions like Tessian that use behavioral intelligence to detect and prevent advanced email attacks, including increasingly sophisticated email-delivered invoice and wire fraud.
To see how the Tessian Intelligent Cloud Email Security platform prevents ransomware attacks, and protects against DLP, watch a product overview video or book a demo.
For the latest cybersecurity news and articles, sign up for our newsletter, and follow us on Twitter and LinkedIn
Charles Brook
Threat Intelligence Specialist