After almost three years of pandemic induced disruption, Black Hat 2022 marked the return to a semblance of normalcy in Las Vegas. The number one hot take from 2022’s show was the hope for the pandemic to finally be behind us.
One aspect, however, that will never be the same again is the rapid shift to distributed computing environments, across the world. This explains why cloud adoption is growing at an unprecedented scale, with Gartner forecasting almost $500 billion will be spent on cloud services in 2022, with the figure rising to nearly $600 billion by 2023.
Increasing complexity and a rapidly expanding attack surface area are some of the main drivers, according to former CISA director Chris Krebs in his opening keynote, of why cyber risk is going to get worse before it gets better. Krebs also called on the cyber community and the government to continue bolstering efforts to address cyber risk.
Phishing and multi-factor authentication compromise
Phishing and multi-factor authentication (MFA) compromise were among the dominant threats covered by established and emerging security vendors at Black Hat 2022. Trying to stay relevant, one of the legacy email security solutions unveiled machine learning capabilities in an attempt to address cyber threats that are increasingly able to bypass secure email gateways (SEGs).
Tessian’s CISO, Josh Yavor and KnowBe4’s Roger Grimes both focussed their Black Hat presentations on the how threat actors are leveraging social engineering to compromise MFA, with Roger underscoring that 70-90% of all breaches are attributed to social engineering, including MFA compromises.
Although MFA remains an important security control, organizations have been prone to placing too much faith in this one particular security measure. Although underscoring the importance of MFA, Roger cautioned against the overstated claims that by adopting MFA an organization is near impenetrable.
Tessian’s Josh illustrated how MFA has become an important security control, but that threat actors are able to compromise it via a range of social engineering attacks. Josh ended his presentation with an appeal – only by adopting advanced anti-phishing solutions, that leverage machine learning powered behavioral intelligence to detect threats as they manifest, can the risk of a credential compromise be reduced.
Some of the other themes observed at Black Hat 2022 included a focus on addressing cloud and end-user cyber risk, with a range of solutions that included contextually aware API security, intelligent vulnerability management, end-user isolation for a hybrid workforce, as well as ensuring that security awareness training actually strengthens security culture.
Cyber risks caused by human error
Coinciding with the annual security conference, several high-profile breaches were trending, including a Lapsus$ ransomware attack on Cisco in early August, as well as Marriott International suffering a third breach since 2018. Both attacks were attributed to employee credential compromise.
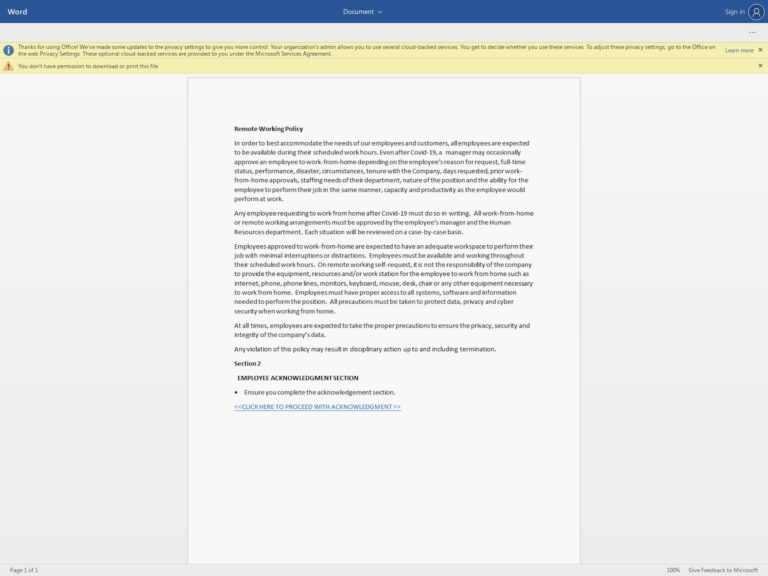
In the case of Cisco, the threat actors compromised an employee’s personal Gmail account and gained access to stored credentials in that account. In the case of Marriott, a month prior to the 2022 Black Hat conference, an employee at one of its hotels provided credentials to a threat actor.
Both instances underscore the reality that people make mistakes and that a layered security strategy is no longer a nice to have but is essential to reducing the risk of a breach. These instances also validate findings from recent seminal industry security reports including IBM’s Cost of a Data Breach 2022 and Verizon’s DBIR 2022 demonstrating that compromise credentials and phishing are the leading threat vectors.
Similar findings have been echoed in the vendor community, most recently by Palo Alto’s Unit 42, showing that 70% of its incident response is attributed to business email compromise and ransomware related attacks.
The future of cybersecurity is in the cloud
Breaches are increasing in frequency as well as costs associated with a compromise, with the average breach cost now costing victims an average of $4.35m. That number jumps to $10.1m if you happen to be in healthcare.
Only by leveraging best-in-breed cloud native security solutions will increasingly advanced attacks be detected and prevented. Cloud native security solutions benefit from not carrying technical debt from an on-premise world, but rather have the advantage of being engineered from the ground-up for adaptive, cloud-based threats.
For example, Tessian’s Intelligent Cloud Email Security Platform has behavioral intelligence at its core – enabled by machine learning, using Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Natural Language Understanding (NLU) – is able to detect threats as they manifest, in real-time. This includes threats that have been able to circumvent initial security controls such as MFA or legacy static, rule-based email security solutions like SEGs.
To see how Tessian prevents ransomware attacks, and protects against DLP, watch a product overview video or book a demo.
For the latest cybersecurity news and articles, sign up for our newsletter, and follow us on Twitter and LinkedIn